The circuit we are gonna talk about today is TRIAC dimmer or some people call it an AC dimmer circuit. Today we are gonna learn how an AC dimming circuit works, how a TRIAC goes into proper working mode and why it is a very useful and important component. Will also show you some different AC dimming circuits and run them out with motors, AC lights or other AC gadgets.
What is a Triac?
A TRIAC component is a bidirectional, three-electrode AC switch which allows the electrons to flow in both directions. It is the same as the two SCRs that are connected in a reverse parallel way with gates connected to each other. A TRIAC is triggered into conduction in both directions by an SCR gate signal. TRIACs were made to prepare means to develop improved AC power controls.
We can get TRIACS in a variety of packaging dispositions. They can work with a wide range of currents and voltages. TRIACs generally have proportionally low current capabilities, if compared to SCRs, they are generally limited to less than 50A and they can’t take over SCRs in high current applications. TRIACs are commonly looked at as versatile because they got the ability to operate with positive or negative voltages covering their terminals. Since SCRs have a disadvantage for conducting current in one direction, thus controlling the low power in an AC circuit is better done by using a TRIAC.
First AC Dimmer
Project

Circuit Diagram
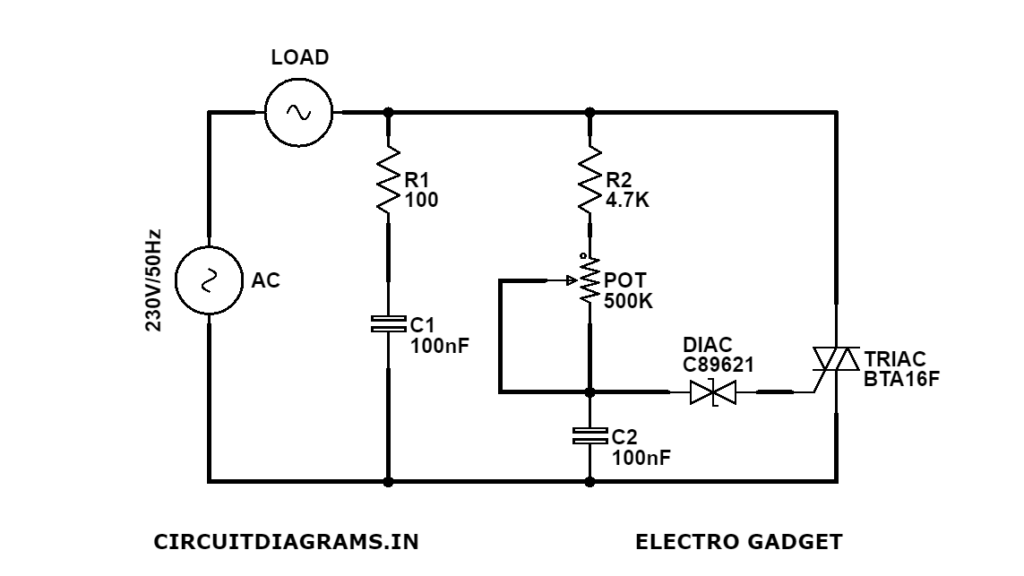
Components Required
- BAT16F TRIAC
- C89621 DIAC
- 500KΩ Potentiometer
- 100nF/400V Capacitor
- 100nF/600V Capacitor
- Resistor (100Ω, 4.7KΩ)
- Connection Wire
- Veroboard
Working Principle of First AC Dimmer Circuit
This AC Dimmer circuit is a perfectly Analog circuit. It got no microcontroller or digital component, only some passive components. Now here comes an easy circuit, which is mentioned above. We have the TRIAC, another component which we know as DIAC, resistors and capacitors. If we wanna change the firing pulse time we have to use a potentiometer and that’s the way we can make changes in the output power. This module here is using the same circuit.
Now that we have no microcontroller, what is applying the pulses on the TRIAC gate with this simple circuit? We have to analyze that. The DIAC component allows current flow in both directions, but only allows that when a certain voltage limit is reached. So we start that with the power off and then we apply the AC voltage at the input. Now the TRIAC is off, the output is still zero. We have a small current flow through the R2 resistor and the potentiometer which will charge the capacitor C1. After the voltage value of the capacitor reaches the limit value of the DIAC, it allows current to flow at the gate of the TRIAC and then it’s activated.
After that, the TRIAC will allow current flow as the output is on till the polarity of the AC voltage changes and the TRIAC is deactivated. But now that small capacitor is charged with a negative polarity as the AC voltage is now set on the negative side. Again, when the capacitor reaches a certain limit value, the DIAC allows current flow once again and activates the gate of TRIAC again.
Now, as you can see, just charging up the small capacitor creates those firing pulses at the TRIAC gate. The charging speed of the capacitor is controlled by the resistor and potentiometer values. The higher the resistor value, the slower the charging process will be, so the firing pulse is applied later, so the output power will be lower. That’s why a potentiometer is used, which can regulate this resistance value thus making the charging procedure faster or slower and thus making the output power change easier.
Second AC Dimmer
Circuit Diagram
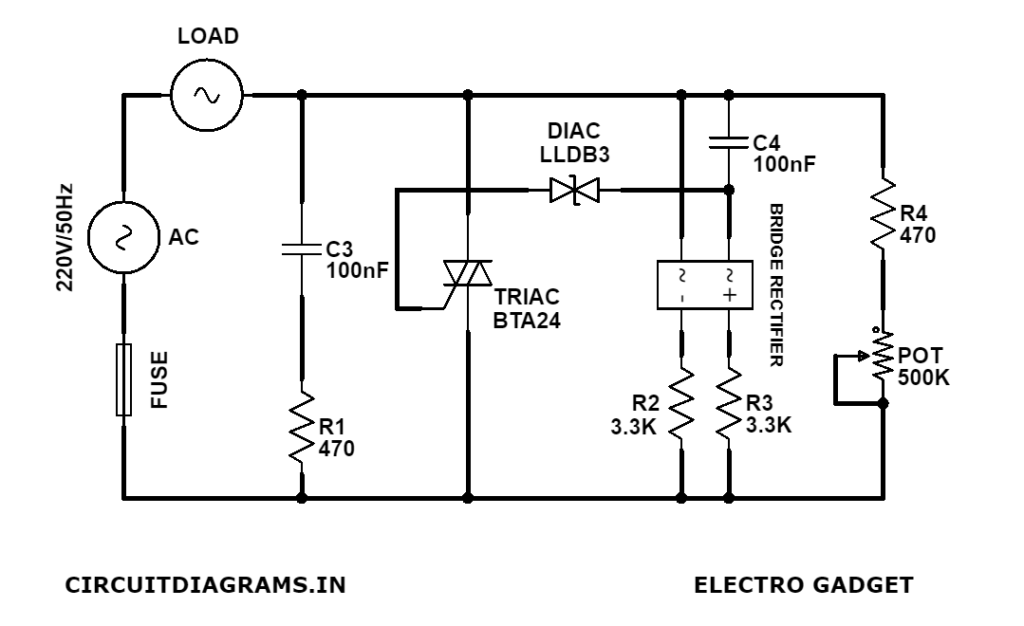
Components Required
- BAT24 TRIAC
- LLDB3 DIAC
- Bridge Rectifier
- 500KΩ Potentiometer
- 100nF/400V Capacitor
- 100nF/600V Capacitor
- 470Ω Resistor (x2)
- 3.3KΩ Resistor (x2)
- Connection Wire
- Veroboard
Working Principle of Second AC Dimmer Circuit
I got a different module here which works like the other one. But it is also a little different as it uses a small full bridge rectifier. I’ve worked on the PCB and did some changes to it and understood its work mechanism, above is a diagram. It looks a lot like the other one, but you should know that for a lot of power the TRIAC gets, hotter because of the power losses. That’s the reason, all AC dimmers have some kind of cooling mechanism to control that heat. The BTA24 for example could work with up to 800V and 25 amps and that’s some huge power. But make sure to verify the datasheet of each and every component before you try to assemble such a circuit.
Keep in mind that the value of the capacitor and the value of the potentiometer will change the firing time. The bigger the value of the capacitor, the slower the charging process will be. And same applies to the resistor used. Generally, we add a fuse to control the maximum power output.
For example, this circuit has a 20 amps fuse. Also, as you can see on the PCB of the module, SMD resistors are used but they are quite big and it is 25 12 packages as they could resist more power. The capacitor which is used should be rated for high voltage and also, it has to be non-polarized because here we are working on AC.